Bringing Deep Learning Workloads to JSC supercomputers course
Alexandre Strube // Sabrina Benassou // Javad Kasravi
November 19, 2024
Communication:
Links for the complimentary parts of this course:
- Event page
- Judoor project page invite
- This document: https://go.fzj.de/dl-in-neuroscience
- Our mailing list for AI news
- Survey at the end of the course
- Virtual Environment template
- SOURCE of the course/slides on Github
Goals for this course:
- Make sure you know how to access and use our machines 👩💻
- Put your data in way that supercomputer can use it fast 💨
- Distribute your ML workload 💪
- Important: This is NOT a basic AI
course 🙇♂️
- If you need one, check fast.ai
Team:



Schedule
| Time | Title |
|---|---|
| 10:00 - 10:10 | Welcome |
| 10:10 - 10:40 | Introduction |
| 10:40 - 11:00 | Jupyter-JSC |
| 11:00 - 11:10 | Coffee Break |
| 11:10 - 11:30 | SLURM |
| 11:30 - 12:00 | Setup Environement |
| 12:00 - 12:10 | Coffee Break |
| 12:10 - 12:40 | Distributed Data Parallel |
| 12:40 - 13:00 | Model Parallelism and Analysis |
Note
Please open this document on your own browser! We will need it for the exercises. https://go.fzj.de/dl-in-neuroscience

Jülich Supercomputers
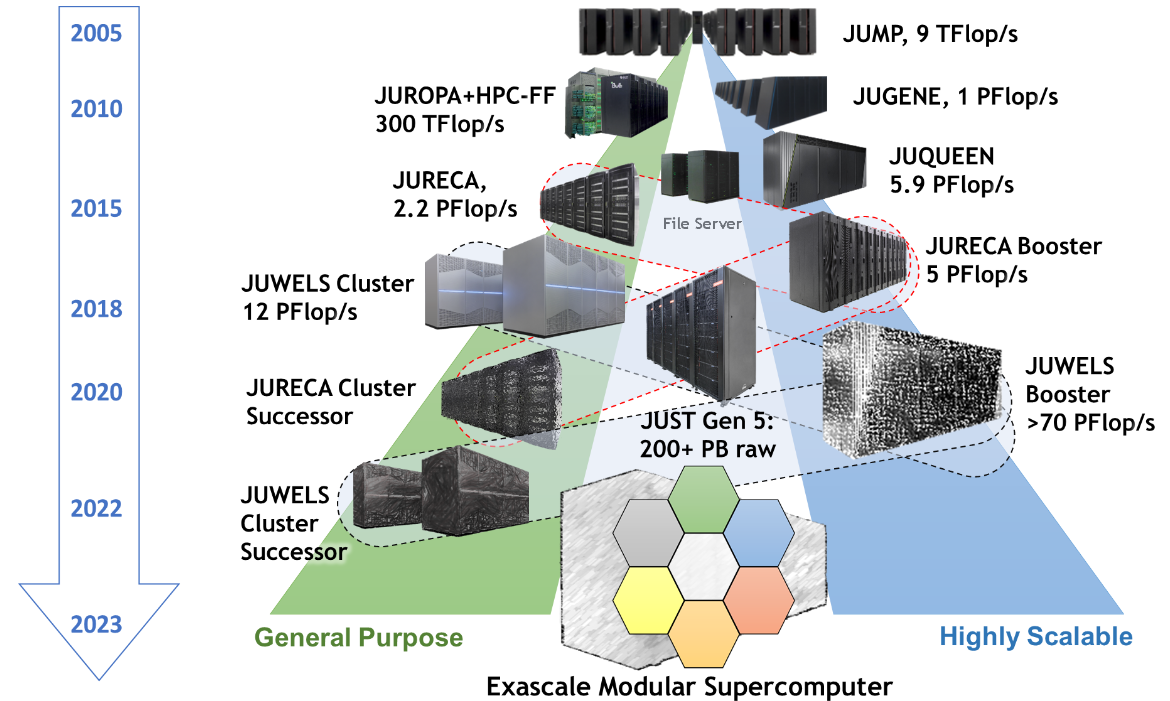
What is a supercomputer?
- Compute cluster: Many computers bound together locally
- Supercomputer: A damn lot of computers bound
together locally😒
- with a fancy network 🤯
Anatomy of a supercomputer
- Login Nodes: Normal machines, for compilation, data transfer, scripting, etc. No GPUs.
- Compute Nodes: Guess what?
- For compute! With GPUs! 🤩
- High-speed, ultra-low-latency network
- Shared networked file systems
- Some numbers we should (more or less) know about
them:
- Nodes
- Cores, Single-core Performance
- RAM
- Network: Bandwidth, Latency
- Accelerators (e.g. GPUs)
JURECA DC Compute Nodes
- 192 Accelerated Nodes (with GPUs)
- 2x AMD EPYC Rome 7742 CPU 2.25 GHz (128 cores/node)
- 512 GiB memory
- Network Mellanox HDR infiniband (FAST💨 and EXPENSIVE💸)
- 4x NVIDIA A100 with 40gb 😻
- TL;DR: 24576 cores, 768 GPUs 💪
- Way deeper technical info at Jureca DC Overview
How do I use a Supercomputer?
- Batch: For heavy compute, ML training
- Interactively: Jupyter
You don’t use the whole supercomputer
You submit jobs to a queue asking for resources
You don’t use the whole supercomputer
And get results back
You don’t use the whole supercomputer
You are just submitting jobs via the login node
You don’t use the whole supercomputer
You are just submitting jobs via the login node
You don’t use the whole supercomputer
You are just submitting jobs via the login node
You don’t use the whole supercomputer
- Your job(s) enter the queue, and wait for its turn
- When there are enough resources for that job, it runs

You don’t use the whole supercomputer
And get results back
Supercomputer Usage Model
- Using the the supercomputer means submitting a job to a batch system.
- No node-sharing. The smallest allocation for jobs is one compute node (4 GPUs).
- Maximum runtime of a job: 24h.
Recap:
- Login nodes are for submitting jobs, move files, compile, etc
- NOT FOR TRAINING NEURAL NETS
Recap:
- User submit jobs
- Job enters the queue
- When it can, it runs
- Sends results back to user
Connecting to Jureca DC
Getting compute time
- Go to https://go.fzj.de/dl-in-neuroscience-project-join
- Join the course project
training2441 - Sign the Usage Agreements (Video)
- Compute time allocation is based on compute projects. For every compute job, a compute project pays.
- Time is measured in core-hours. One hour of Jureca DC is 128 core-hours.
- Example: Job runs for 8 hours on 64 nodes of Jureca DC: 8 * 64 * 128 = 65536 core-h!
Jupyter-jsc
- Jupyter-JSC uses the queue
- When you are working on it, you are using project time ⌛️
- Yes, if you are just thinking and looking at the 📺, you are burning project time🤦♂️
- It’s useful for small tests - not for full-fledged development 🙄
Jupyter-jsc
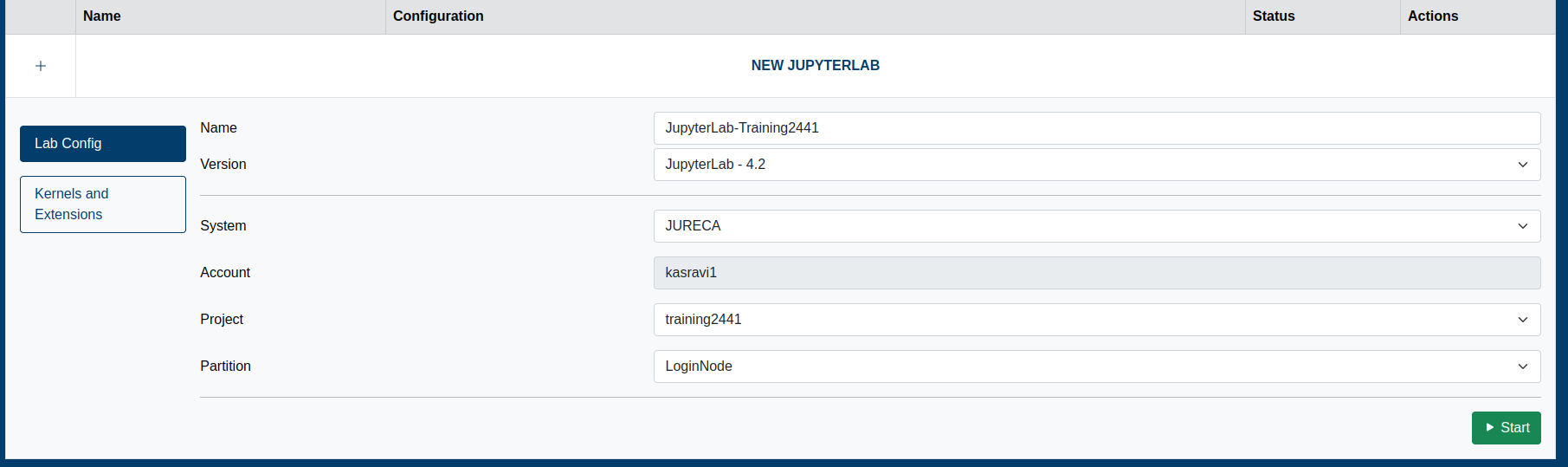
Working with the supercomputer’s software
- We have literally thousands of software packages, hand-compiled for the specifics of the supercomputer.
- Full list
- Detailed documentation
Luncher in Jupyter-JSC
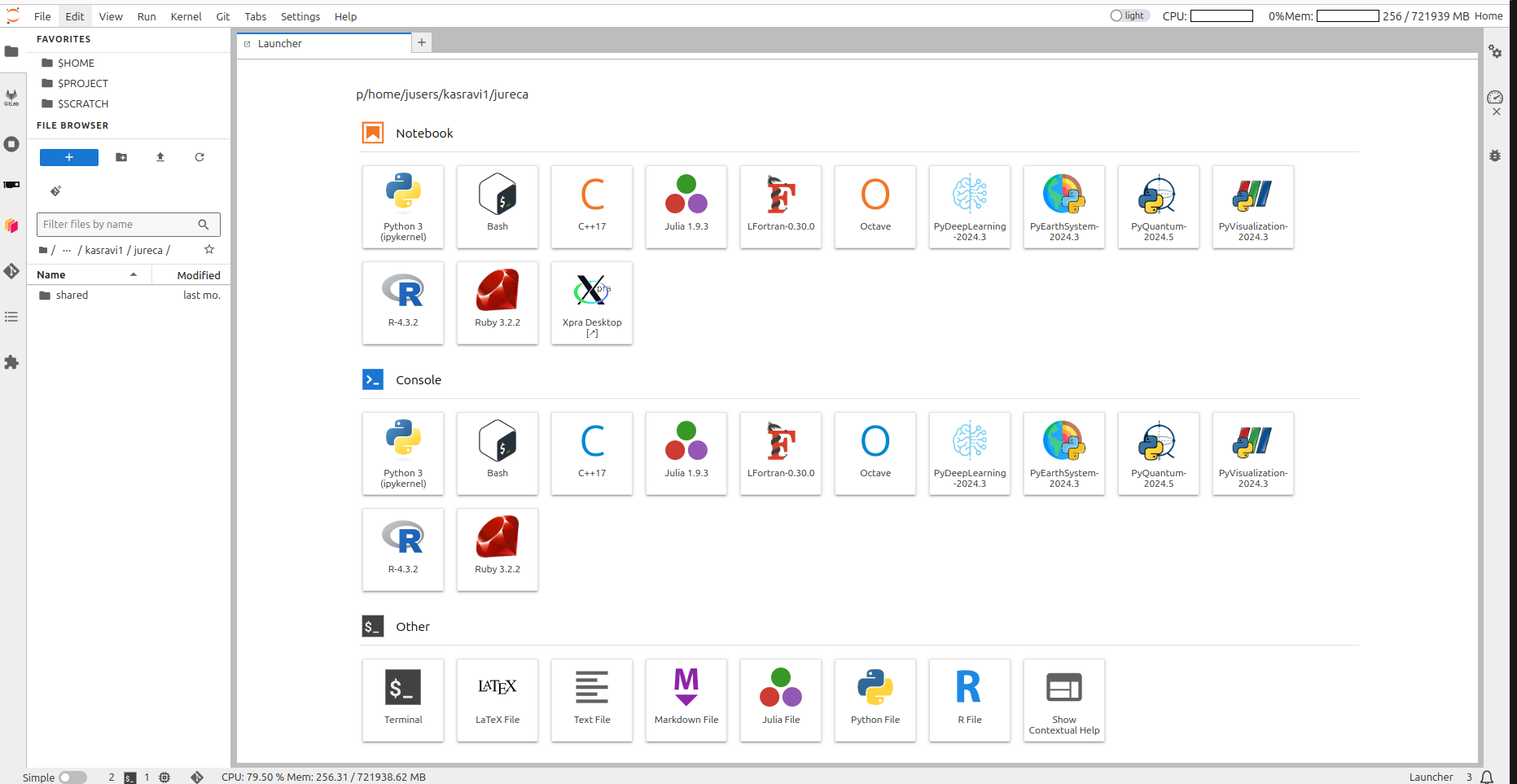
Software
Connect to terminal
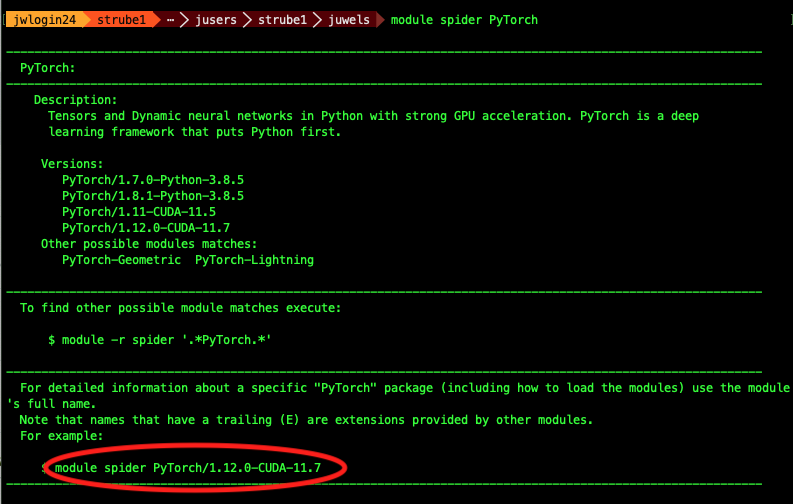
Tool for finding
software: module spider
strube1$ module spider PyTorch
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PyTorch:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Description:
Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration.
PyTorch is a deep learning framework that puts Python first.
Versions:
PyTorch/1.7.0-Python-3.8.5
PyTorch/1.8.1-Python-3.8.5
PyTorch/1.11-CUDA-11.5
PyTorch/1.12.0-CUDA-11.7
Other possible modules matches:
PyTorch-Geometric PyTorch-Lightning
...What do we have?
module avail (Inside hierarchy)
Module hierarchy
Stage (full collection of software of a given year)
Compiler
MPI
Module
Eg:
module load Stages/2023 GCC OpenMPI PyTorch
What do I need to load such software?
module spider Software/version
Example: PyTorch
Search for the software itself - it will suggest a version
Example: PyTorch
Search with the version - it will suggest the hierarchy
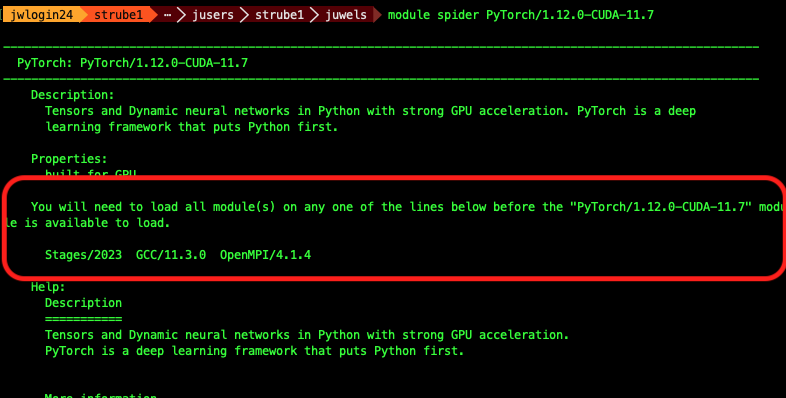
Example: PyTorch
Copy and paste these lines
module load Stages/2024
module load GCC OpenMPI Python PyTorch
# And we run a small test: import pytorch and ask its version
python -c "import torch ; print(torch.__version__)" Should look like this:
Python Modules
Some
of the python softwares are part of Python itself, or of other
softwares. Use “module key”
module key toml
The following modules match your search criteria: "toml"
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Jupyter: Jupyter/2020.2.5-Python-3.8.5, Jupyter/2021.3.1-Python-3.8.5, Jupyter/2021.3.2-Python-3.8.5, Jupyter/2022.3.3, Jupyter/2022.3.4
Project Jupyter exists to develop open-source software, open-standards, and services for interactive computing across dozens of programming languages.
PyQuil: PyQuil/3.0.1
PyQuil is a library for generating and executing Quil programs on the Rigetti Forest platform.
Python: Python/3.8.5, Python/3.9.6, Python/3.10.4
Python is a programming language that lets you work more quickly and integrate your systems more effectively.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------How to run it on the login node
create a python file
create a python file
create an python file
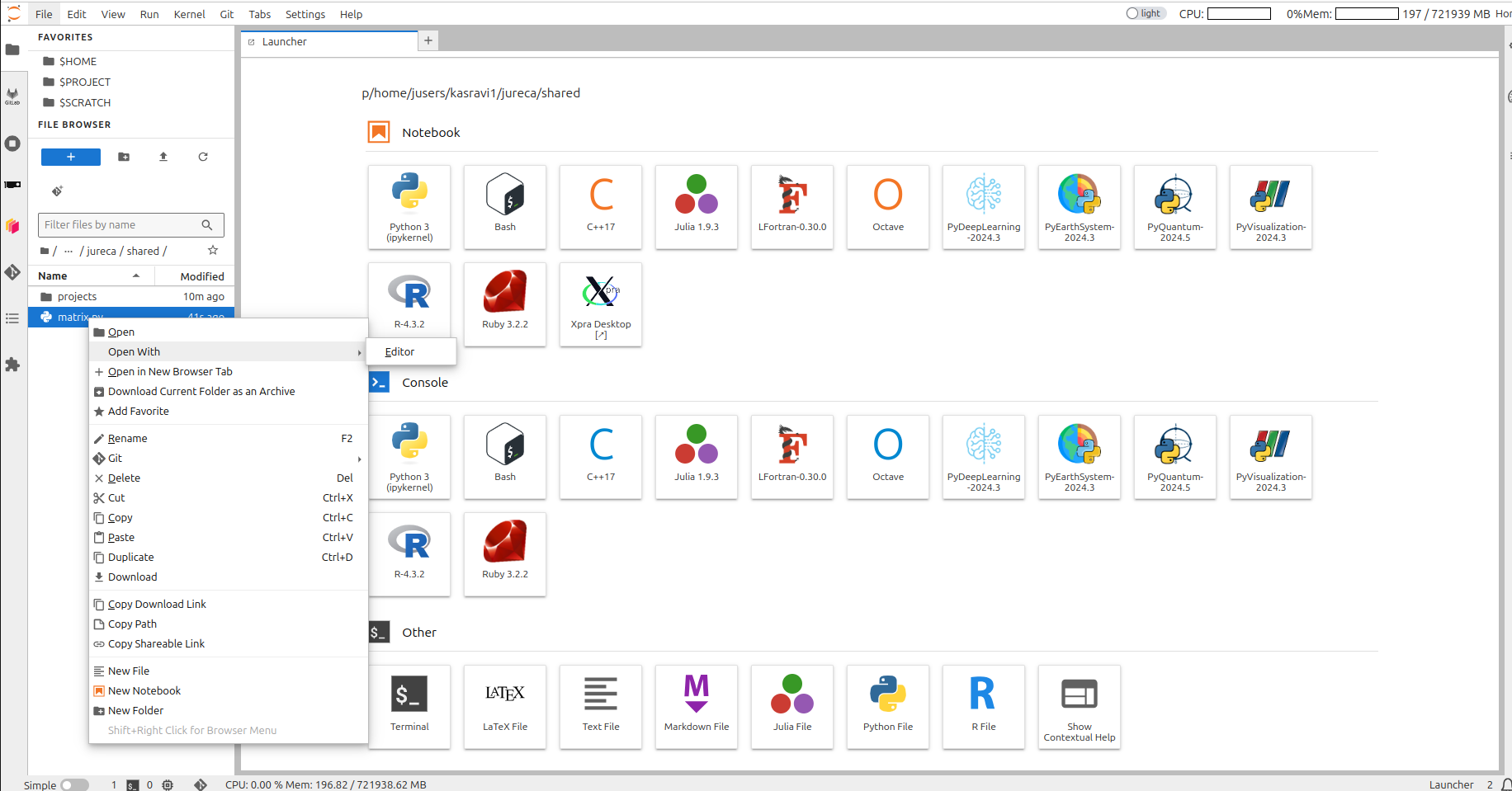
create a python file
create a python file
Run code in login node
module load Stages/2023
module load GCC OpenMPI PyTorch
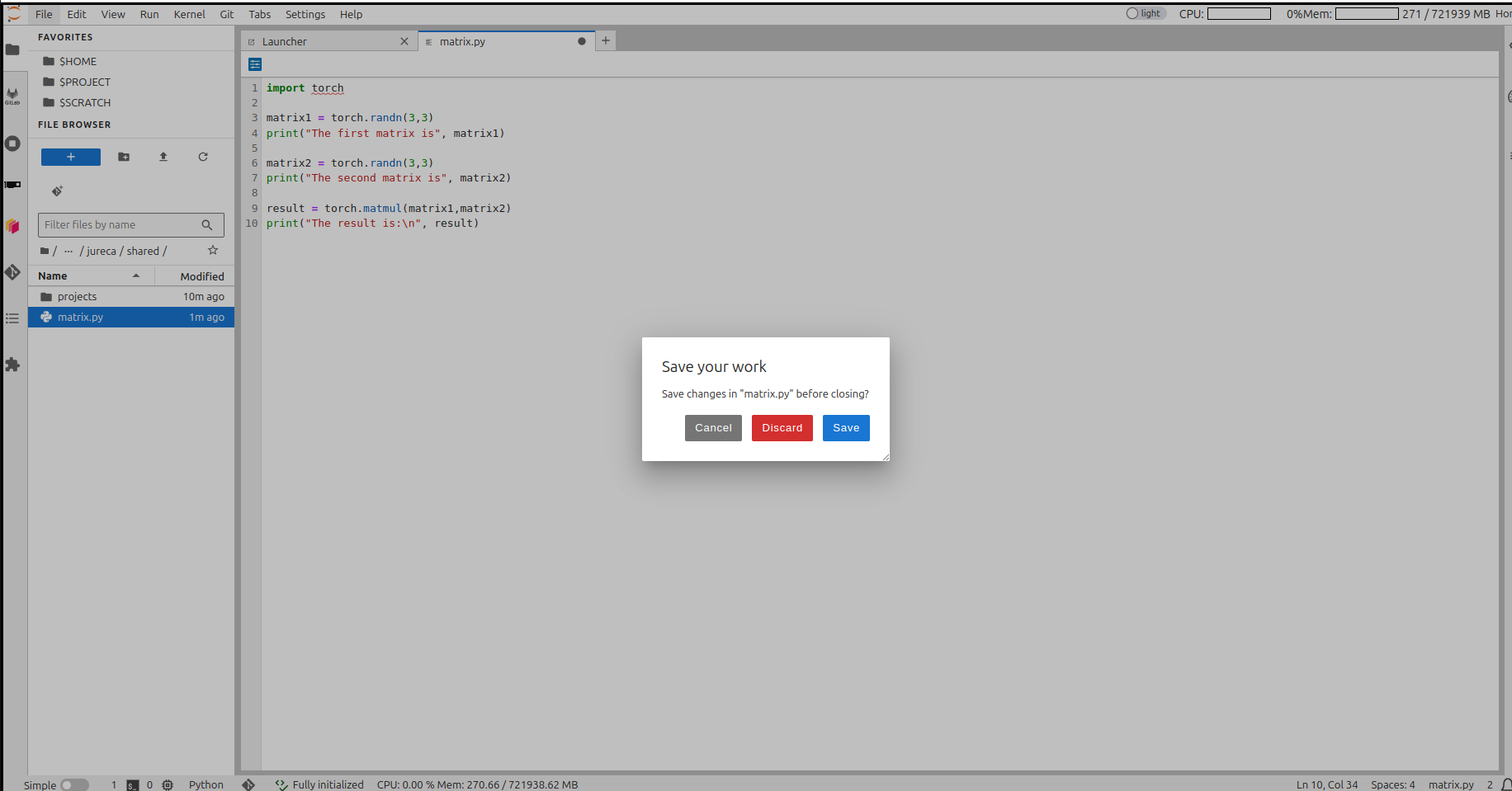
python matrix.pyBut that’s not what we want… 😒
So we send it to the queue!
HOW?🤔
SLURM 🤯

Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management
Slurm submission file
- Simple text file which describes what we want and how much of it, for how long, and what to do with the results
Slurm submission file example
Create a file named jureca-matrix.sbatch as described in
the previous section, and copy all the content from the following into
this file.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account=training2441 # Who pays?
#SBATCH --nodes=1 # How many compute nodes
#SBATCH --job-name=matrix-multiplication
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # How many mpi processes/node
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # How many cpus per mpi proc
#SBATCH --output=output.%j # Where to write results
#SBATCH --error=error.%j
#SBATCH --time=00:01:00 # For how long can it run?
#SBATCH --partition=dc-gpu # Machine partition
#SBATCH --reservation=training2441 # For today only
module load Stages/2024
module load GCC OpenMPI PyTorch # Load the correct modules on the compute node(s)
srun python matrix.py # srun tells the supercomputer how to run itSubmitting a job: SBATCH
Are we there yet?

Are we there yet? 🐴
squeue --me
squeue --me
JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
412169 gpus matrix-m strube1 CF 0:02 1 jsfc013ST is status:
- PD (pending),
- CF(configuring),
- R (running),
- CG (completing)
Reservations
- Some partitions have reservations, which means that only certain users can use them at certain times.
- For this course, it’s called
training2441
Job is wrong, need to cancel
Check logs
By now you should have output and error log files on your directory. Check them!
simply open output.412169 and error.412169
using Editor !!
Setup project path
mkdir $PROJECT_training2441/$USER
Create a shortcut for the project on the home folder
rm -rf ~/course ; ln -s $PROJECT_training2441/$USER ~/course
# Enter course folder and
cd ~/course
# Where am I?
pwd
# We well need those later
mkdir ~/course/.cache
mkdir ~/course/.config
mkdir ~/course/.fastai
rm -rf $HOME/.cache ; ln -s ~/course/.cache $HOME/
rm -rf $HOME/.config ; ln -s ~/course/.config $HOME/
rm -rf $HOME/.fastai ; ln -s ~/course/.fastai $HOME/Extra software, modules and kernels
You want that extra
software from pip….
Example: Let’s install some software!
- Even though we have PyTorch, we don’t have PyTorch Lightning Flash
- Same for fast.ai and wandb
- We will install them in a virtual environment
Example: Let’s install some software!
Edit the file sc_venv_template/requirements.txt
Add these lines at the end:
Run on the terminal:
sc_venv_template/setup.sh
Example: Activating the virtual environment
Example: Activating the virtual environment
Let’s train a 🐈 classifier!
This is a minimal demo, to show some quirks of the supercomputer
Create a file “cats.py”
from fastai.vision.all import * from fastai.callback.tensorboard import * # print("Downloading dataset...") path = untar_data(URLs.PETS)/'images' print("Finished downloading dataset") # def is_cat(x): return x[0].isupper() # Create the dataloaders and resize the images dls = ImageDataLoaders.from_name_func( path, get_image_files(path), valid_pct=0.2, seed=42, label_func=is_cat, item_tfms=Resize(224)) print("On the login node, this will download resnet34") learn = vision_learner(dls, resnet34, metrics=accuracy) cbs=[SaveModelCallback(), TensorBoardCallback('runs', trace_model=True)] # Trains the model for 6 epochs with this dataset learn.unfreeze() learn.fit_one_cycle(6, cbs=cbs)
Submission file for the classifier
create file fastai.sbatch
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --account=training2441
#SBATCH --mail-user=MYUSER@fz-juelich.de
#SBATCH --mail-type=ALL
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --job-name=cat-classifier
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=128
#SBATCH --output=output.%j
#SBATCH --error=error.%j
#SBATCH --time=00:20:00
#SBATCH --partition=dc-gpu
#SBATCH --reservation=training2441 # For today only
source sc_venv_template/activate.sh # Now we finally use the fastai module
srun python cats.pySubmit it
Submission time
- Check error and output logs, check queue
Probably not much happening…
💥
What happened?
- It might be that it’s not enough time for the job to give up
- Check the
error.${JOBID}file - If you run it longer, you will get the actual error:
🤔…
What is it doing?
- This downloads the dataset:
- And this one downloads the pre-trained weights:
Remember, remember
Remember, remember
Compute nodes have no internet connection
- But the login nodes do!
- So we download our dataset before…
- On the login nodes!
On the login node:
- Comment out the line which does AI training:
- Call our code on the login node!
Run the downloader on the login node
$ source sc_venv_template/activate.sh
$ python cats.py
Downloading dataset...
|████████-------------------------------| 23.50% [190750720/811706944 00:08<00:26]
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-b627a593.pth" to /p/project/ccstao/cstao05/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/resnet34-b627a593.pth
100%|█████████████████████████████████████| 83.3M/83.3M [00:00<00:00, 266MB/s]Run it again on the compute nodes!
- Un-comment back the line that does training:
- Submit the job!
Masoquistically waiting for the job to run?
(To exit, type CTRL-C)
Check output files
- You can see them within jupyter-jsc
The activation script must be sourced, otherwise the virtual environment will not work. Setting vars Downloading dataset... Finished downloading dataset epoch train_loss valid_loss error_rate time Epoch 1/1 : |-----------------------------------| 0.00% [0/92 00:00<?] Epoch 1/1 : |-----------------------------------| 2.17% [2/92 00:14<10:35 1.7452] Epoch 1/1 : |█----------------------------------| 3.26% [3/92 00:14<07:01 1.6413] Epoch 1/1 : |██---------------------------------| 5.43% [5/92 00:15<04:36 1.6057] ... .... Epoch 1/1 : epoch train_loss valid_loss error_rate time 0 0.049855 0.021369 0.007442 00:42- 🎉
- 🥳
Tools for results analysis
- We already ran the code and have results
- To analyze them, there’s a neat tool called Tensorboard
- And we already have the code for it on our example!
Example: Tensorboard
Open a notebook
Choose PyDeepLearning-2024.3 kernel
Write
Example: Tensorboard
Port Forwarding
Tensorboard on Jureca DC
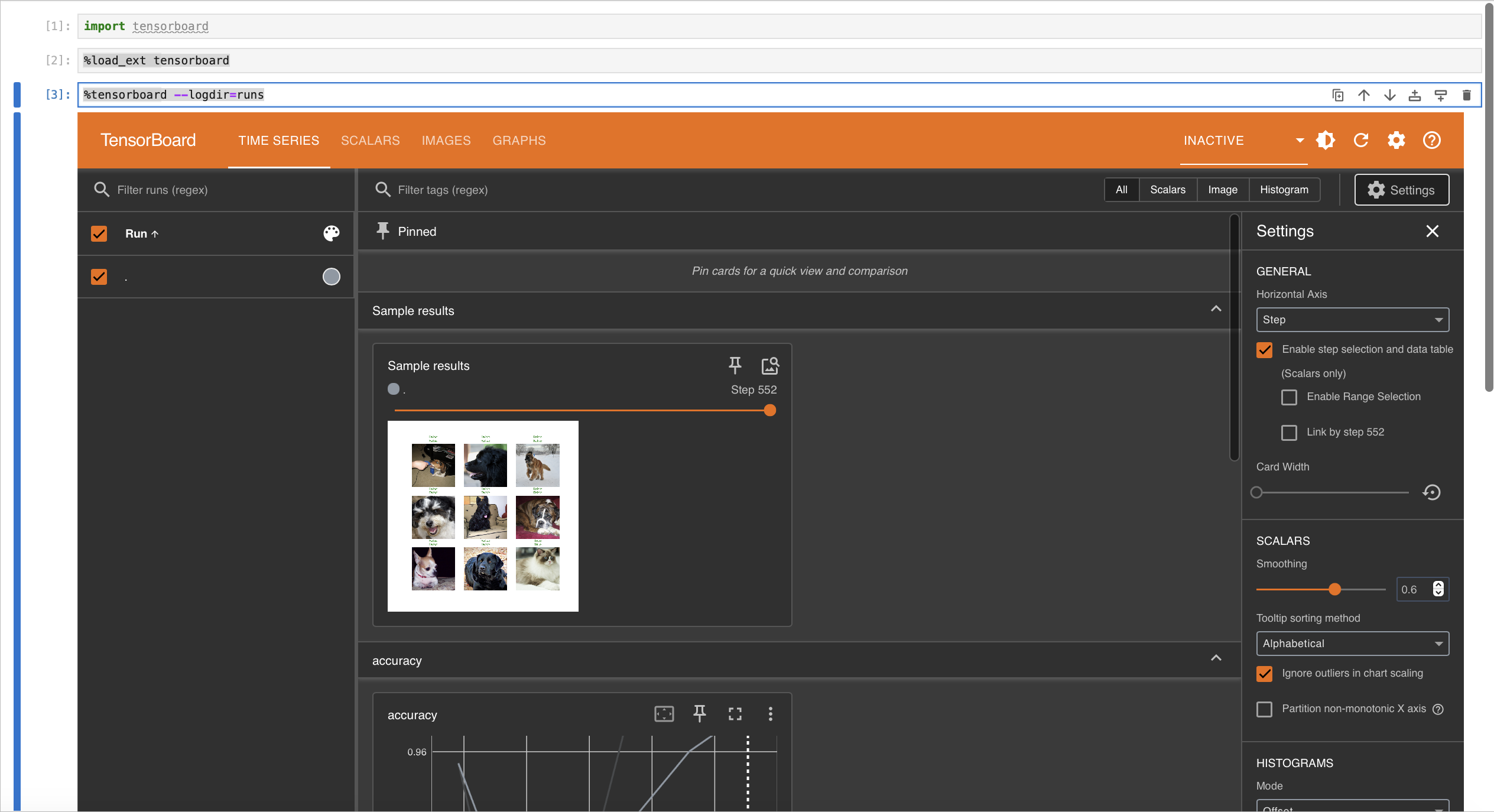
Part 1 recap
As of now, I expect you managed to:
- Stay awake for the most part of this morning 😴
- A working connection to the supercomputers 🖥️
- Can edit and transfer files via jupyter-jsc 📝
- Submit jobs and read results 📫
- Access web services on the login nodes 🧙♀️
- Is ready to make great code! 💪