Parallelize Training
Parallelize Training
Alexandre Strube // Sabrina Benassou
October 17, 2023
We need to download some code
The ImageNet dataset
Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)
- An image dataset organized according to the WordNet hierarchy.
- Extensively used in algorithms for object detection and image classification at large scale.
- It has 1000 classes, that comprises 1.2 million images for training, and 50,000 images for the validation set.

ImageNet class
root = "/p/scratch/training2336/data/"
with open(os.path.join(root, "train_data.pkl"), "rb") as f:
train_data = pickle.load(f)
train_samples = list(train_data.keys())
train_targets = list(train_data.values())train_samples = ['ILSVRC/Data/CLS-LOC/train/n03146219/n03146219_8050.JPEG',
'ILSVRC/Data/CLS-LOC/train/n03146219/n03146219_12728.JPEG',
'ILSVRC/Data/CLS-LOC/train/n03146219/n03146219_9736.JPEG',
'ILSVRC/Data/CLS-LOC/train/n03146219/n03146219_22069.JPEG',
...]
train_targets = [524,
524,
524,
524,
...]ImageNet class
class ImageNet(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root, transform=None):
self.root = root
with open(os.path.join(self.root, "train_data.pkl"), "rb") as f:
train_data = pickle.load(f)
self.samples = list(train_data.keys())
self.targets = list(train_data.values())
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.samples)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
x = Image.open(os.path.join(self.root, self.samples[idx])).convert("RGB")
if self.transform:
x = self.transform(x)
return x, self.targets[idx]PyTorch Lightning Data Module
class ImageNetDataModule(pl.LightningDataModule):
def __init__(
self,
data_root: str,
batch_size: int,
num_workers: int,
dataset_transforms: dict(),
):
super().__init__()
self.data_root = data_root
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.num_workers = num_workers
self.dataset_transforms = dataset_transforms
def setup(self, stage: Optional[str] = None):
self.train = ImageNet(self.data_root, self.dataset_transforms)
def train_dataloader(self):
return DataLoader(self.train, batch_size=self.batch_size, \
num_workers=self.num_workers)PyTorch Lightning Module
class resnet50Model(pl.LightningModule):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.model = resnet50(pretrained=False)
def forward(self, x):
return self.model(x)
def training_step(self,batch):
x, labels = batch
pred=self.forward(x)
train_loss = F.cross_entropy(pred, labels)
self.log("training_loss", train_loss)
return train_loss
def configure_optimizers(self):
return torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=0.02)One GPU training
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Resize((256, 256))
])
# 1. Organize the data
datamodule = ImageNetDataModule("/p/scratch/training2336/data/", 256, \
int(os.getenv('SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK')), transform)
# 2. Build the model
model = resnet50Model()
# 3. Create the trainer
trainer = pl.Trainer(max_epochs=10, accelerator="gpu")
# 4. Train the model
trainer.fit(model, datamodule=datamodule)
# 5. Save the model!
trainer.save_checkpoint("image_classification_model.pt")One GPU training
#!/bin/bash -x
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:1
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=96
#SBATCH --time=06:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=booster
#SBATCH --account=training2336
#SBATCH --output=%j.out
#SBATCH --error=%j.err
#SBATCH --reservation=dl4neurosc
# To get number of cpu per task
export SRUN_CPUS_PER_TASK="$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK"
# activate env
source $HOME/course/$USER/sc_venv_template/activate.sh
# run script from above
time srun python3 gpu_training.pyDEMO
But what about many GPUs?
- It’s when things get interesting
Data Parallel
Data Parallel
Data Parallel - Averaging
Multi-GPU training
1 node and 4 GPU
#!/bin/bash -x
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4 # Use the 4 GPUs available
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=4 # When using pl it should always be set to 4
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=24 # Divide the number of cpus (96) by the number of GPUs (4)
#SBATCH --time=02:00:00
#SBATCH --partition=booster
#SBATCH --account=training2336
#SBATCH --output=%j.out
#SBATCH --error=%j.err
#SBATCH --reservation=dl4neurosc
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 # Very important to make the GPUs visible
export SRUN_CPUS_PER_TASK="$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK"
source $HOME/course/$USER/sc_venv_template/activate.sh
time srun python3 gpu_training.pyDEMO
Now, What’s about multi-node training?
Data Parallel - Multi Node
Data Parallel - Multi Node
Before we go further…
- Data parallel is usually good enough 👌
- If you need more than this, you should be giving this course, not me 🤷♂️
Parallel Training with PyTorch DDP
- PyTorch’s
DDP (Distributed Data Parallel) works as follows:
- Each GPU across each node gets its own process.
- Each GPU gets visibility into a subset of the overall dataset. It will only ever see that subset.
- Each process inits the model.
- Each process performs a full forward and backward pass in parallel.
- The gradients are synced and averaged across all processes.
- Each process updates its parameters.
Terminologies
- WORLD_SIZE: number of processes participating in the job.
- RANK: the rank of the process in the network.
- LOCAL_RANK: the rank of the process on the local machine.
- MASTER_PORT: free port on machine with rank 0.
DDP steps
- Set up the environement variables for the distributed mode (WORLD_SIZE, RANK, LOCAL_RANK …)
DDP steps
- Initialize a sampler to specify the sequence of indices/keys used in data loading.
- Implements data parallelism of the model.
- Allow only one process to save checkpoints.
DDP steps
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Resize((256, 256))
])
# 1. The number of nodes
nnodes = os.getenv("SLURM_NNODES")
# 2. Organize the data
datamodule = ImageNetDataModule("/p/scratch/training2336/data/", 128, \
int(os.getenv('SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK')), transform)
# 3. Build the model using desired Task
model = resnet50Model()
# 4. Create the trainer
trainer = pl.Trainer(max_epochs=10, accelerator="gpu", num_nodes=nnodes)
# 5. Train the model
trainer.fit(model, datamodule=datamodule)
# 6. Save the model!
trainer.save_checkpoint("image_classification_model.pt")DDP training
16 nodes and 4 GPU each
#!/bin/bash -x
#SBATCH --nodes=16 # This needs to match Trainer(num_nodes=...)
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4 # Use the 4 GPUs available
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=4 # When using pl it should always be set to 4
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=24 # Divide the number of cpus (96) by the number of GPUs (4)
#SBATCH --time=00:15:00
#SBATCH --partition=booster
#SBATCH --account=training2336
#SBATCH --output=%j.out
#SBATCH --error=%j.err
#SBATCH --reservation=dl4neurosc
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 # Very important to make the GPUs visible
export SRUN_CPUS_PER_TASK="$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK"
source $HOME/course/$USER/sc_venv_template/activate.sh
time srun python3 ddp_training.pyDDP training
With 4 nodes:
With 8 nodes:
With 16 nodes:
With 32 nodes:
Data Parallel
- It was
- Became
Data Parallel
- It was
- Became
#SBATCH --nodes=16 # This needs to match Trainer(num_nodes=...) #SBATCH --gres=gpu:4 # Use the 4 GPUs available #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=4 # When using pl it should always be set to 4 #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=24 # Divide the number of cpus (96) by the number of GPUs (4) export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 # Very important to make the GPUs visible
DEMO
That’s it for data parallel!
- Copy of the model on each GPU
- Use different data for each GPU
- Everything else is the same
- Average after each epoch
- Update of the weights
TensorBoard
- In resnet50.py
![]()
TensorBoard
import random
MYPORT = random.randint(10000, 15000)
%load_ext tensorboard
%tensorboard --logdir lightning_logs/ --port $MYPORT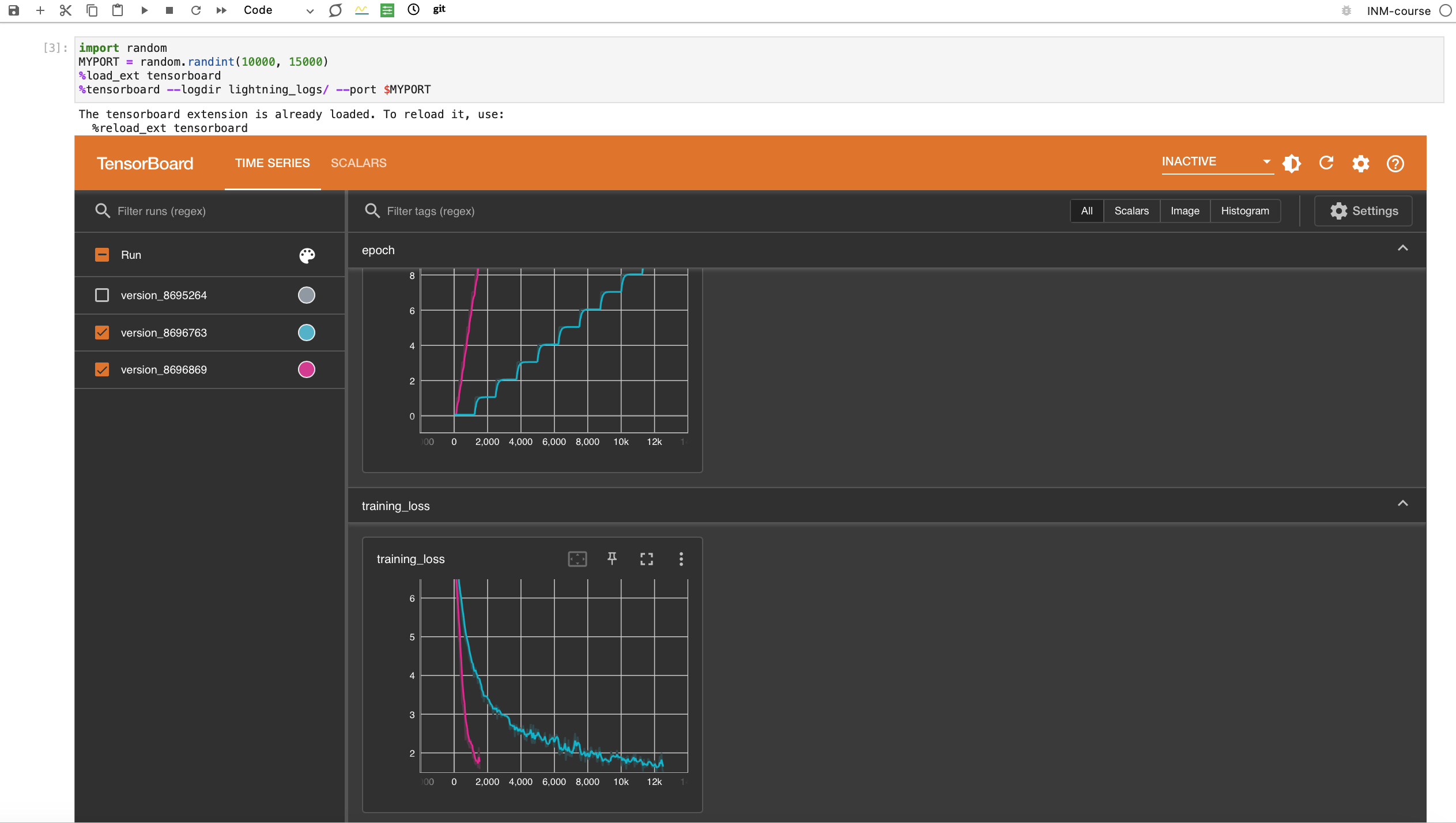
DEMO
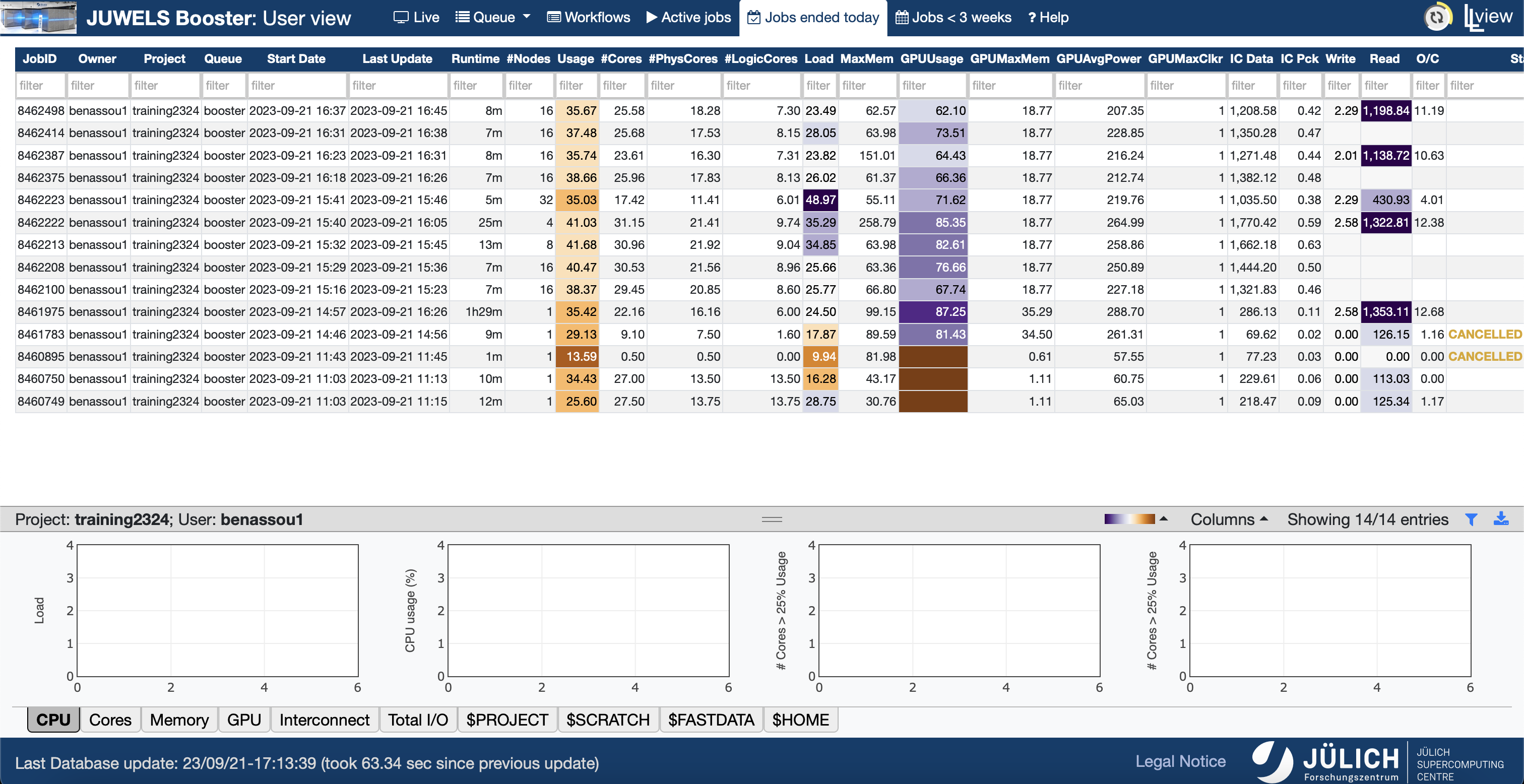
Llview
- llview
- https://go.fzj.de/llview-juwelsbooster
![]()
RECAP
- Ran parallel code.
- Can submit single node, multi-gpu and multi-node training.
- Use TensorBoard on the supercomputer.
- Usage of llview.